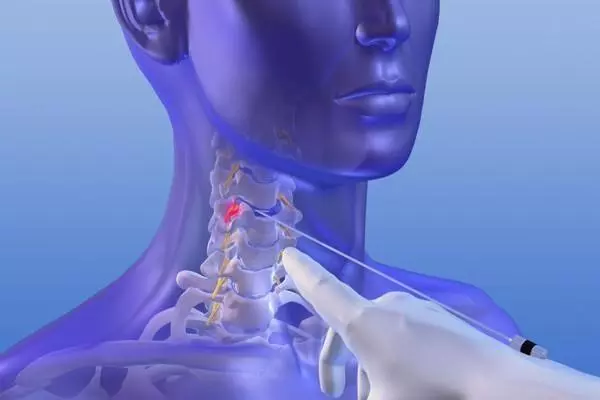
Intervertebral disc surgery
(percutaneously on the cervical spine)
In this endoscopic disc surgery, the entire disc is not removed and replaced with a placeholder (cage, bone block or prosthesis), as is usually the case, but only the herniated disc is removed under local anesthesia. The natural mobility and stability of the cervical spine is thus retained.
Ultimately, this intervertebral disc surgery (percutaneous nucleotomy) is performed in the same way as intervertebral disc surgery in the lumbar spine area, where only the herniated disc is removed and not the entire intervertebral disc is replaced by an artificial placeholder.
This revolutionary surgical technique is used almost exclusively by Dr. Schubert performed.
Do you have any complaints?
Then use our online questionnaire - professional initial assessment in 48 hours
Endoscopic disc surgery
If severe pain and neurological symptoms cannot be controlled with conservative means, surgical repair of the herniated disc is necessary. The aim of the endoscopic disc surgery is to remove the pressurized disc tissue and thus to relieve the pinched nerve spatially or to lay it completely free again. For a long time, surgical stiffening of the affected segment was considered the gold standard for repairing a herniated disc in the cervical spine – a procedure that requires an open approach and as a result of which the affected segment permanently loses its mobility.
With endoscopic disc surgery / disc surgery (nucleotomy), we have a low-risk alternative to open microsurgical disc surgery, which causes spatial relief in the disc space without opening the spinal canal or having to stiffen the affected segment. In this way, the fine nerve structures are spared and overloading of the adjacent intervertebral discs - a frequent consequence of the stiffening operation - is avoided. Because only very little tissue has to be removed overall, there is almost no scarring in the surgical area.
This procedure is not to be confused with similar-sounding so-called "percutaneous procedures" in which healthy tissue is shrunk and/or removed merely by heat or suction of disc core material, in the belief that the herniated disc will recede. This is not a standard operation.
The difference in this procedure is that under X-ray control, specially developed instruments are placed exactly at the point where the herniated disc presses on the nerve root and this is then removed. The rest of the healthy intervertebral disc tissue is left!
How does the treatment of the endoscopic intervertebral disc surgery work?
Under local anesthesia (in rare cases under general anesthesia), a thin probe is first inserted percutaneously into the affected intervertebral disc space under X-ray control. Special miniature instruments are then advanced directly to the incident via this probe. The protruding intervertebral disc tissue can now be precisely removed using small grasping forceps.
The effect: the stressed nerve root is exposed again, so that the pain subsides almost immediately. In some cases it is necessary to shrink the nucleus of the disc with the help of enzyme (chymopapain) in order to support the healing process of the disc fibrous ring.
Overall, the procedure takes about 30 to 45 minutes.
A medical check-up takes place one day after the operation and you can leave the clinic again. After 3 months, a clinical radiological check-up is carried out.
The percutaneous intervertebral disc surgery
on the cervical spine - modified Frykholm
With this surgical technique, access is from behind (dorsal). The dorsal cervical microforaminotomy (Frykholm operation) is a tissue-sparing, low-risk surgical procedure.
In particular, with the new minimally invasive approaches for the so-called soft lateral (side) sequestration, and to a lesser extent for purely lateral foramen stenosis, it represents an effective alternative to ventral discectomy with subsequent fusion or with the subsequent implantation of an intervertebral disc prosthesis (spinal arthroplasty). the additional use of an endoscope can be helpful. The method of posterior percutaneous intervertebral disc surgery achieves a high success rate if the indication is correct.
In this endoscopic disc surgery, the entire disc is not removed and replaced with a placeholder (cage, bone block or prosthesis), as is usually the case, but only the herniated disc is removed under local anesthesia. The natural mobility and stability of the cervical spine is thus retained.
What aftercare is required?
In the first week you should take it easy; however, wearing a neck brace is not required. About a week after the operation, it is advisable to start physiotherapy tailored to your individual needs under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
When can you do sports again?
You should be able to swim or cycle regularly again about three weeks after the procedure. You can gradually resume your usual sporting training about six weeks after the procedure.
When are you able to work again?
After one to two weeks, you can resume office work and light physical work. You should avoid heavy physical activity for the first six weeks and then slowly increase it.
What is the success rate?
The success rate in our own investigations and studies is over 90 percent.
At a glance!
| The most important facts and data are summarized and compared for you at a glance | ||
|---|---|---|
| Conventional open disc surgery of the cervical spine |
Percutaneous or endoscopic disc surgery of the cervical spine |
|
| anesthesia | The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Danger of surgical nerve damage | The operation is usually performed under local anesthesia. The patient is continuously monitored and put into a kind of twilight sleep. Nerve damage is therefore practically impossible. |
| storage | The patient lies on his back, the neck is positioned overstretched and a skin incision of approx. 4 - 8 cm is made | The patient is in the supine position and a stab incision no larger than 0.3 cm is made with the neck comfortably positioned |
| risk |
|
|
| Pains | The level of pain after the operation (neck pain) tends to be very high. | After percutaneous or endoscopic disc surgery, there is little or no pain |
| After the procedure |
|
|
| hospital stay | A stay in the clinic of 1-3 weeks may be required before the procedure | 2-4 days |
| surgery | Depending on the surgical method, healthy structures are destroyed. Depending on the type of intervention, an additional incision on the iliac crest is necessary to remove bone material. In the course of this fusion, the corresponding segments are fixed with plates and screws. Loss of movement as well as severe traumatization and the resulting pain are the result | Only the disturbing and prolapsed disc tissue is removed without damaging surrounding structures such as bones, ligaments or muscles. Thus, the natural stability and mobility is maintained. The formation of dreaded scar tissue is also avoided |
| Sports | Sport is only possible after approx. 4 - 6 weeks | Sport is already possible again after 1-2 weeks |
| meeting | Long waiting times are not uncommon | In acute cases, you can be operated on within 48 hours |
!!! The mobility and functionality of the spine is fully preserved !!!
The advantages of percutaneous intervertebral disc surgery at a glance:
- very low infection rate <0.01%
- This minimally invasive procedure preserves the natural stability and mobility of the intervertebral disc
(of the movement segment) fully preserved - Because hardly any tissue is destroyed, the procedure is less stressful and the risk of complications is low
- The operation is performed under local anesthesia
- No longer hospital stay is necessary: you can go home one day after the operation.
If you wish, the procedure can also be performed on an outpatient basis, so that you can leave the hospital on the same day - You can go back to your usual activities just a few days after the operation
- A short convalescence: After one to two weeks you are able to work again,
after about six weeks you can go back to your usual sports - The procedure leaves almost no scars
- According to our own statistical evaluations, the success rate is around 90%