What is kyphosis of the spine?
Basically, there are different types of deformities of the spine.
In addition to the so-called kyphosis (increased hunchback formation, e.g. M. Scheuermann or widow's hump in osteoporotic multiple vertebral fractures or in M. Bechterew), kyphosis in older people is probably the most well-known and most common deformity of the spine.
What causes kyphosis?
- idiopathic kyphoses (most common, approx. 85% of all kyphoses)
- congenital (congenital) kyphoses
- Metabolic kyphosis
- myogenic kyphosis
- Kyphoses in M. Scheuermann or M. Bechterew
In idiopathic kyphoses
Kyphoses tend to increase in childhood. Correct posture, especially while sitting, is important!
Common complaints
In childhood and adolescence, scoliosis, depending on the degree of severity, usually does not cause any or only very rarely symptoms in the sense of back pain.
- Back pain radiating down the leg
- Severe discomfort when walking longer distances
Sometimes no more 100 meters possible without a longer break - Numbness in the buttocks and/or legs
- Aggravation of pain in stretched posture
- Your pain is relieved by bending over or sitting down
Careful diagnosis is a prerequisite for successful treatment
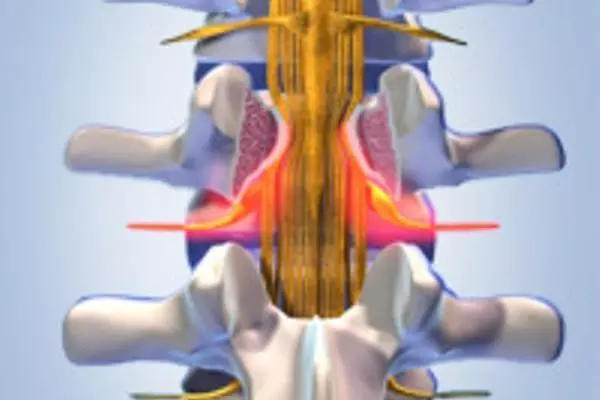
Which procedure makes sense in individual cases depends on the diagnosis. Although the description of the symptoms usually points the way, clarity is often only brought about by imaging procedures such as computer or magnetic resonance imaging. It is important to know the degree of spinal damage and to know how many segments are affected by the narrowing. It is also important to determine whether there is already instability in the spine, whether and to what extent bony outgrowths must be surgically removed, or whether the desired relief can be achieved, for example, with the use of an implant.
In principle, any section of the spine can be affected by a narrowing; by far the most commonly affected area is the lumbar spine.
How is it treated?
- Conservative treatment